개요
리눅스 내장 명령어 top를 구현한 프로그램이다. top 명령어와 동일하게 3초 단위로 새로 갱신되며, 방향키 및 q 입력으로 Column / Row 이동 및 종료를 할 수 있다.
실행 방법
$make ttop
./ttop
기능
-
기본 실행
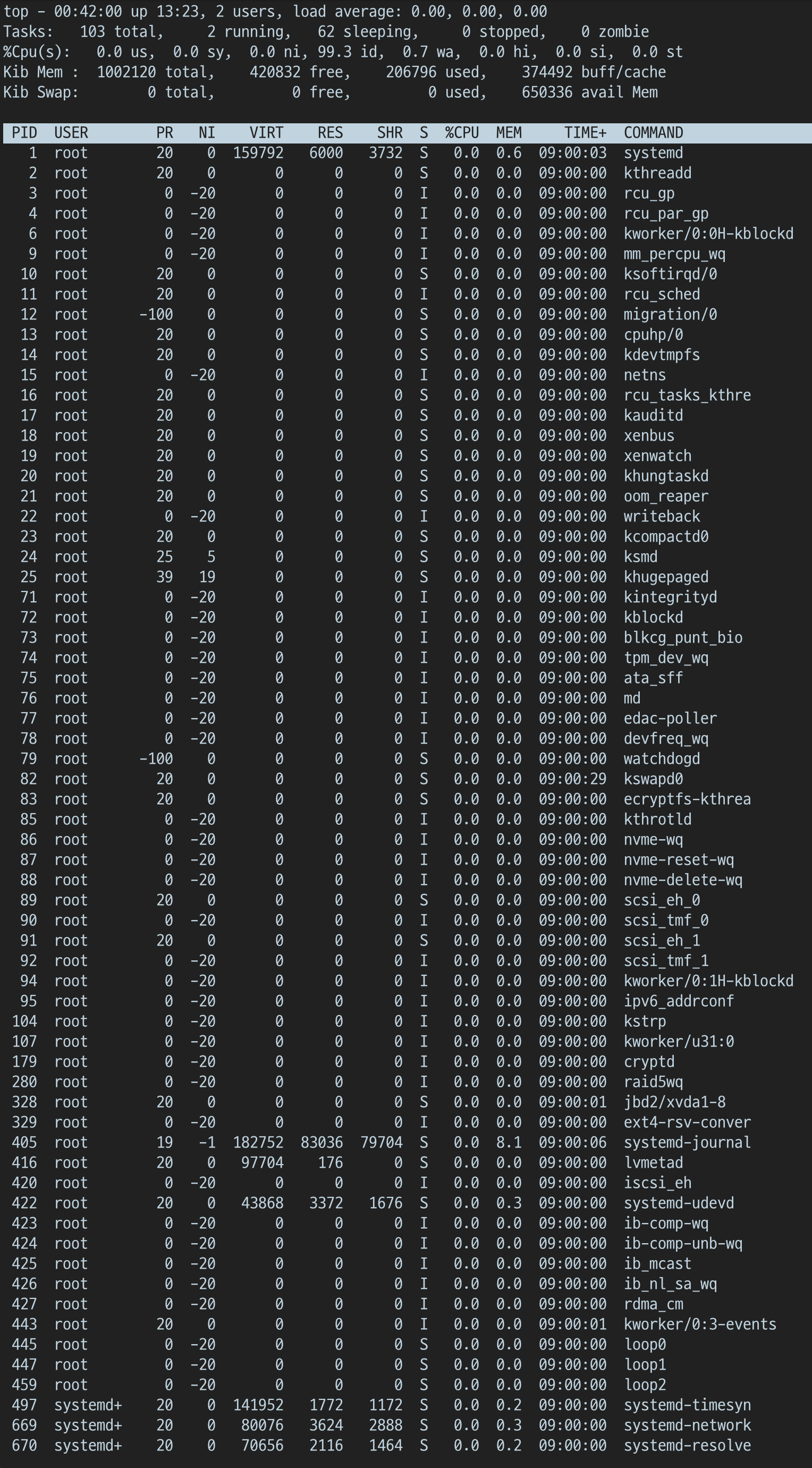
-
상하 방향키 입력 통한 Row 이동
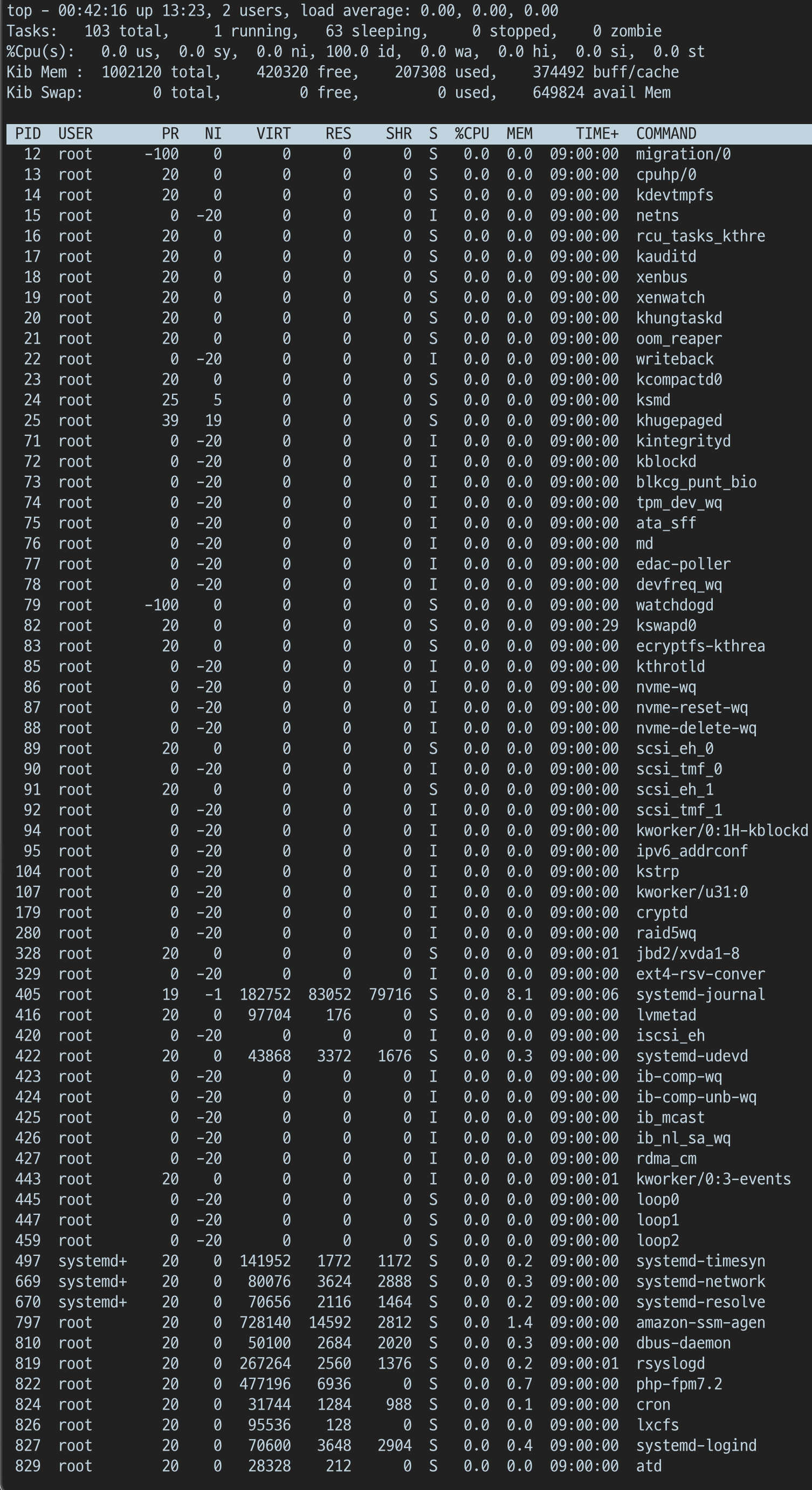
-
좌우 방향키 입력 통한 Column 이동
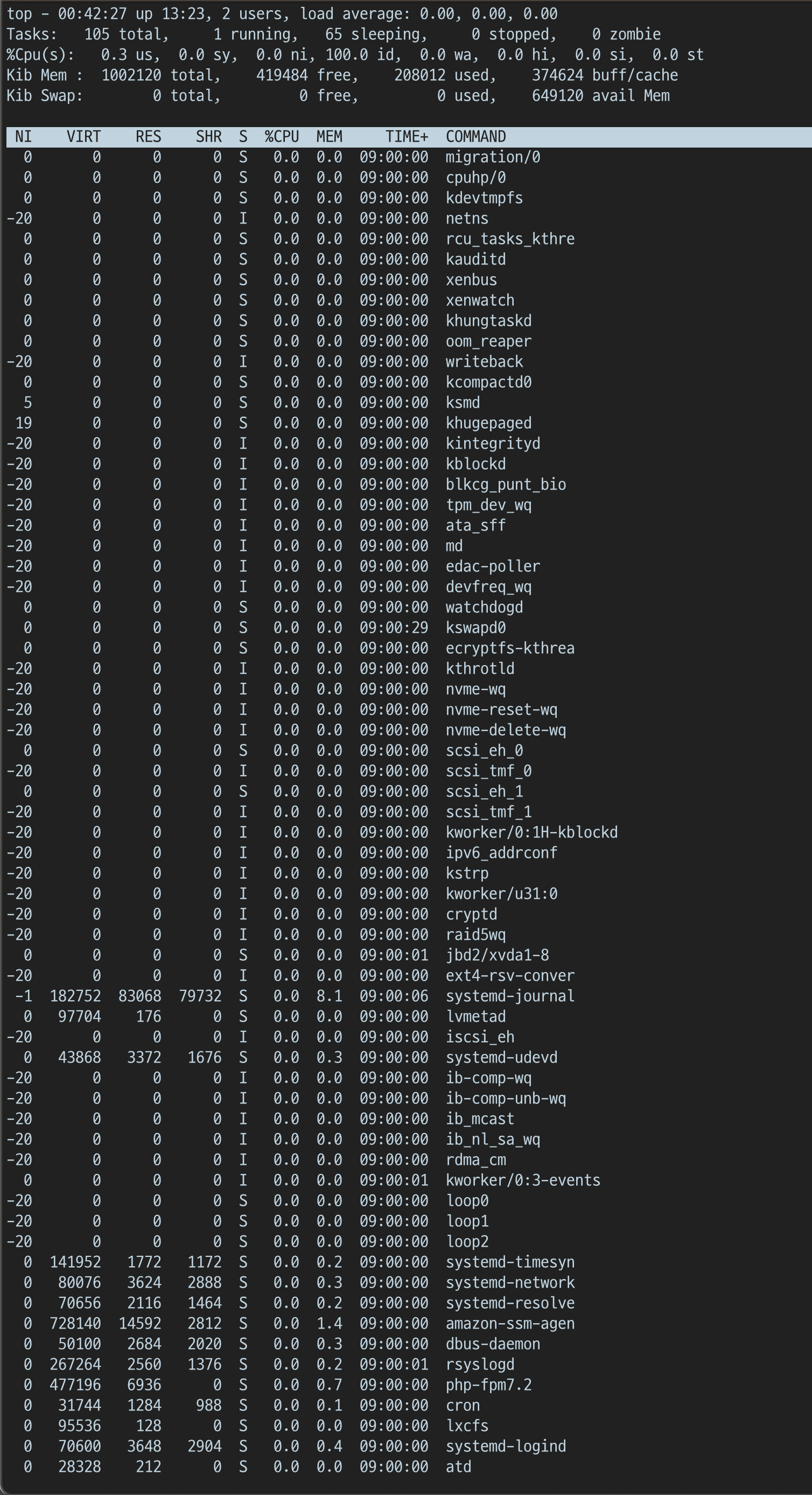
구현 방법
top 명령어의 모든 정보들은 Linux File System에서 얻을 수 있다. 아래는 각각의 항목들에 대한 설명과 값의 출처(Linux File System에서의 파일)들을 작성한 것이다. 프로세스를 추상화한 myProc 구조체를 정의하고, 얻어낸 정보들을 통해 각 프로세스 당 하나의 myProc 인스턴스를 생성했다.
//process를 추상화 한 myProc 구조체
typedef struct{
unsigned long pid;
unsigned long uid; //USER 구하기 위한 uid
char user[UNAME_LEN]; //user명
long double cpu; //cpu 사용률
long double mem; //메모리 사용률
unsigned long vsz; //가상 메모리 사용량
unsigned long rss; //실제 메모리 사용량
unsigned long shr; //공유 메모리 사용량
int priority; //우선순위
int nice; //nice 값
char tty[TTY_LEN]; //터미널
char stat[STAT_LEN]; //상태
char start[TIME_LEN]; //프로세스 시작 시각
char time[TIME_LEN]; //총 cpu 사용 시간
char cmd[CMD_LEN]; //option 없을 경우에만 출력되는 command (short)
char command[CMD_LEN]; //option 있을 경우에 출력되는 command (long)
}myProc;
1행
- boot time: OS 부팅 시각
- /proc/stat의 5행 2번째 token + 1970년 1월 1일
- uptime: OS 부팅 이후 지난 시각
- /proc/uptime의 1번째 token
-
User 수: active login session (터미널에 로그인한 active user의 수)
#include <utmp.h> struct utmp *ut; int userCnt = 0; setutmp(); // /proc/utmp 처음부터 읽기 while((ut = getutent()) != NULL) // /var/usr/utmp에서 utent 읽어들이기 if(ut->ut_type == USER_PROCESS) // /ut_type이 USER일 경우에만 count userCnt++; - load average: 최근 1분/5분/15분 간 평균 실행/대기 중 프로세스 수의 비율
- /.proc/loadavg의 1,2,3번째 token
2행
- 각 State를 갖는 프로세스 수
3행 (CPU)
- 가장 최근 refresh 이후로부터의 CPU 사용률 (첫 실행 시에는 OS 시작 이후)
- us (user): time running un-niced user processes
- /proc/stat의 1행 1번째 token
- sy (system): time running kernel processes
- /proc/stat의 1행 3번째 token
- ni (nice): time running niced user processes
- /proc/stat의 1행 2번째 token
- id (idle): time spent in the kernel idle handler
- /proc/stat의 1행 4번째 token
- wa (IO-wait): time waiting for I/O completion
- /proc/stat의 1행 5번째 token
- hi (hardware interrupts): time spent servicing hardware interrupts
- /proc/stat의 1행 6번째 token
- si (software interrupts): time spent servicing software interrupts
- /proc/stat의 1행 7번째 token
- st (stolen time): time stolen from this vm by the hypervisor
- /proc/stat의 1행 8번째 token
4~5행 (Memory)
- Memory 사용량
- /proc/meminfo의 단위는 모두 kb(1000byte)인 반면, 출력해야 하는 단위는 kib(1024byte)이기 때문에 단위 변환을 수행해야 한다.
- Mem total: 전체 물리 메모리 크기
- /proc/meminfo의 MemTotal (1행)
- Mem free: Free된 메모리 크기
- /proc/meminfo의 MemFree(2행)
- Mem used: 사용 중인 메모리 크기
- /proc/meminfo의 MemTotal(1행)-MemFree(2행)-Buffers(4행)-Cached(5행)-SReclaimable(24행)
- buff/cache: buffer / Cache 메모리 크기
- /proc/meminfo의 Buffers(4행)+Cache(5행)+SReclaimable(24행)
- Swap total: 전체 Swap 메모리 크기
- /proc/meminfo의 SwapTotal(15행)
- Swap free: Swap에서 Free된 메모리 크기
- /proc/meminfo의 SwapFree(16행)
- Swap used: Swap에서 사용중인 메모리 크기
- SwapTotal(14행)-SwapFree(16행)
- avail Mem: 사용 가능한 메모리 크기
- /proc/meminfo의 MemAvailable(3행)
Process
- 각 프로세스의 pid를 이름으로 하는 디렉터리가 /proc에 존재한다. 해당 디렉터리 내에서 정보를 획득한다.
- PID: 프로세스 ID
- /proc/pid/stat의 1번째 token
- USER: 프로세스 소유자명
-
/proc/pid/stat 파일의 uid 알아낸 뒤 uid에서 유저명 획득
#include <sys/types.h> #include <pwd.h> struct stat statbuf; stat("/proc/pid/stat", &statbuf); struct passwd *upasswd = getpwuid(statbuf.st_uid); char user[32]; strcpy(user, upasswd->pwd_name);
- PR: 실행 우선 순위(Priority)
- /proc/pid/stat의 18번째 token
- NI: 실행 우선 순위 관련 NICE 값
- /proc/pid/stat의 19번째 token
- VIRT: 가상 메모리 사용량 (SWAP+RES)
- /proc/pid/status의 VmSize(18행)
- RES: 물리 메모리 사용량
- /proc/pid/status의 VmHWM(21행)
- SHR :공유 메모리 사용량
- /proc/pid/status의 RssFile(24행)
- S: 프로세스 상태(State)
- /proc/pid/stat 3번째 token
-
각 문자 별 상세 정보
D uninterruptible sleep (usually IO) R running or runnable (on run queue) S interruptible sleep (waiting for an event to complete) T stopped by job control signal t stopped by debugger during the tracing W paging (not valid since the 2.6.xx kernel) X dead (should never be seen) Z defunct ("zombie") process, terminated but not reaped by its parent
- %CPU: CPU 사용률
- ((utime+stime) / hertz) / (uptime-(startTime/hertz)) * 100
- utime: User Mode에서 프로세스가 사용한 jiffies(clock ticks)
- /proc/pid/stat의 14번째 token
- stime: Kernel Mode에서 프로세스가 사용한 jiffies(clock ticks)
- /proc/pid/stat의 15번째 token
- startTime: OS 부팅 후 프로세스 시작까지의 jiffies(clock ticks)
- /proc/pid/stat의 22번째 token
- uptime: OS 부팅 후 지난 시간(second)
- /proc/uptime의 1번째 token
-
hertz: 1초 간 일어나는 문맥교환 횟수
#include <unistd.h> int hertz = (int)sysconf(_SC_CLK_TCK);
- %MEM: 메모리 사용률
- RES / memTotal
- RES: 물리 메모리 사용량
- /proc/pid/status의 VmHWM(21행)
- memTotal: 전체 메모리 크기
- /proc/meminfo의 1행 (kib를 kb로 변환해 사용)
- RES: 물리 메모리 사용량
- RES / memTotal
- TIME+: CPU 사용 시간 (0.01초 단위)
- (utime+stime) / (hertz / 100)
- utime: User Mode에서 프로세스가 사용한 jiffies(clock ticks)
- /proc/pid/stat의 14번째 token
- stime: Kernel Mode에서 프로세스가 사용한 jiffies(clock ticks)
- /proc/pid/stat의 15번째 token
-
hertz: 1초 간 일어나는 문맥교환 횟수
#include <unistd.h> int hertz = (int)sysconf(_SC_CLK_TCK);
- utime: User Mode에서 프로세스가 사용한 jiffies(clock ticks)
- (utime+stime) / (hertz / 100)
- COMMAND: 프로세스 실행 시 입력된 명령어
- proc/pid/cmdline